Disease Areas & Products
Tuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB) is caused by a bacteria (Mycobacterium Tuberculosis) that most often affect the lungs. While TB is curable and preventable, it is still one of the top 10 causes of death worldwide. In 2017, 10 million people fell ill with TB; of which 1 million were children. Multidrug-resistant (MDR) TB is reaching crisis levels threating the health security of people. The world-wide effort is on to eradicate TB by the year 2030.
The Risks of Tuberculosis
Tuberculosis mostly affects adults in their most productive years. However, all age groups are at risk. Over 95% of cases and deaths are in developing countries. TB occurs in every part of the world. In 2017, the largest number of new TB cases occurred in the South-East Asia and Western Pacific regions, with 62% of new cases, followed by the African region, with 25% of new cases.
Smear Microscopy Misses Nearly Every Second Positive TB Case
Symptoms & Diagnosis
When a person develops active TB disease, the symptoms (such as cough, fever, night sweats, or weight loss) may be mild for many months. This can lead to delays in seeking care, and results in transmission of the bacteria to others. People with active TB can infect 10 to 15 other people through close contact over the course of a year. Many countries still rely on a long-used method called sputum smear microscopy to diagnose TB. Trained laboratory technicians look at sputum samples under a microscope to see if TB bacteria are present. Microscopy detects only half the number of TB cases and cannot detect drug-resistance.
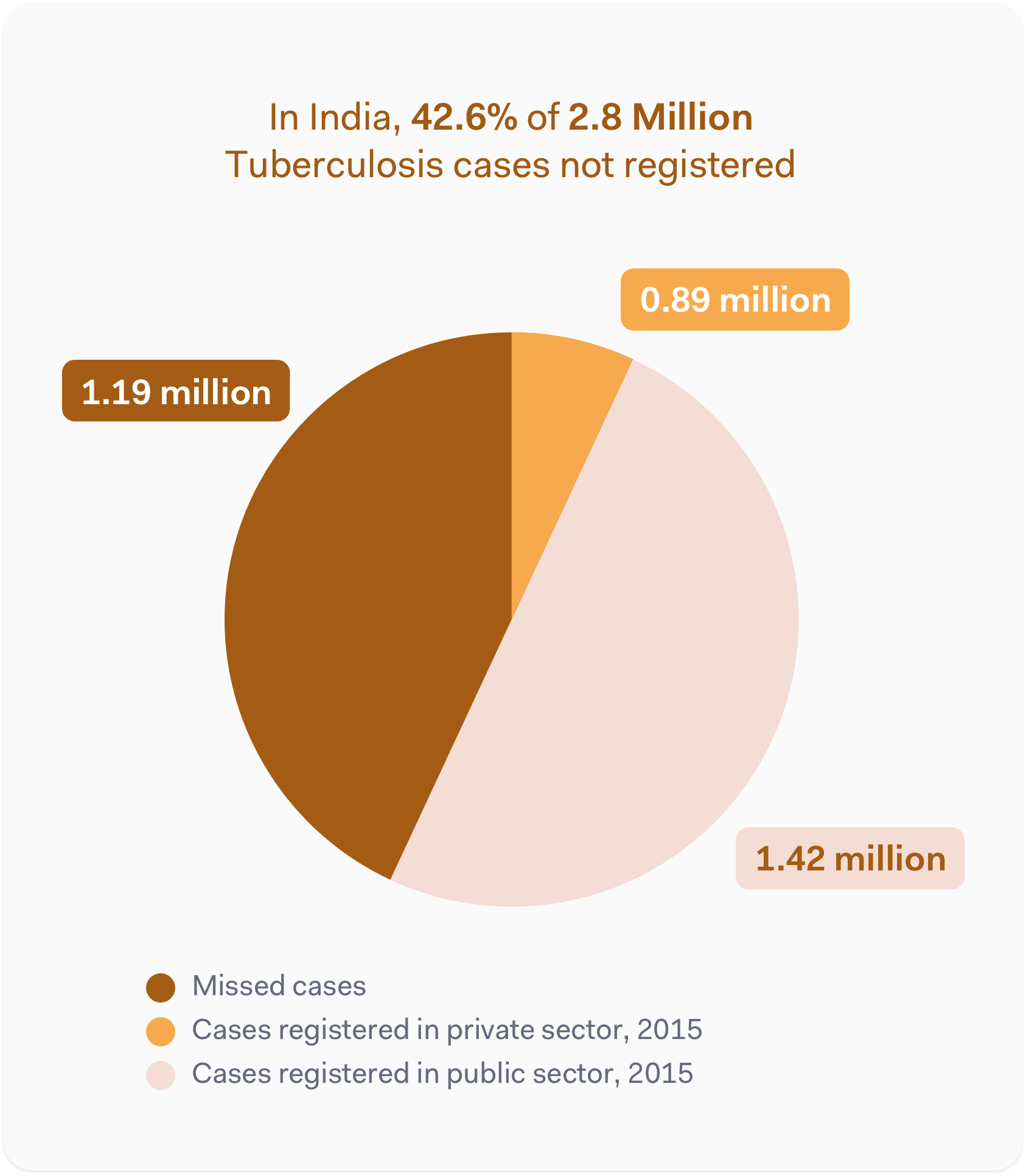
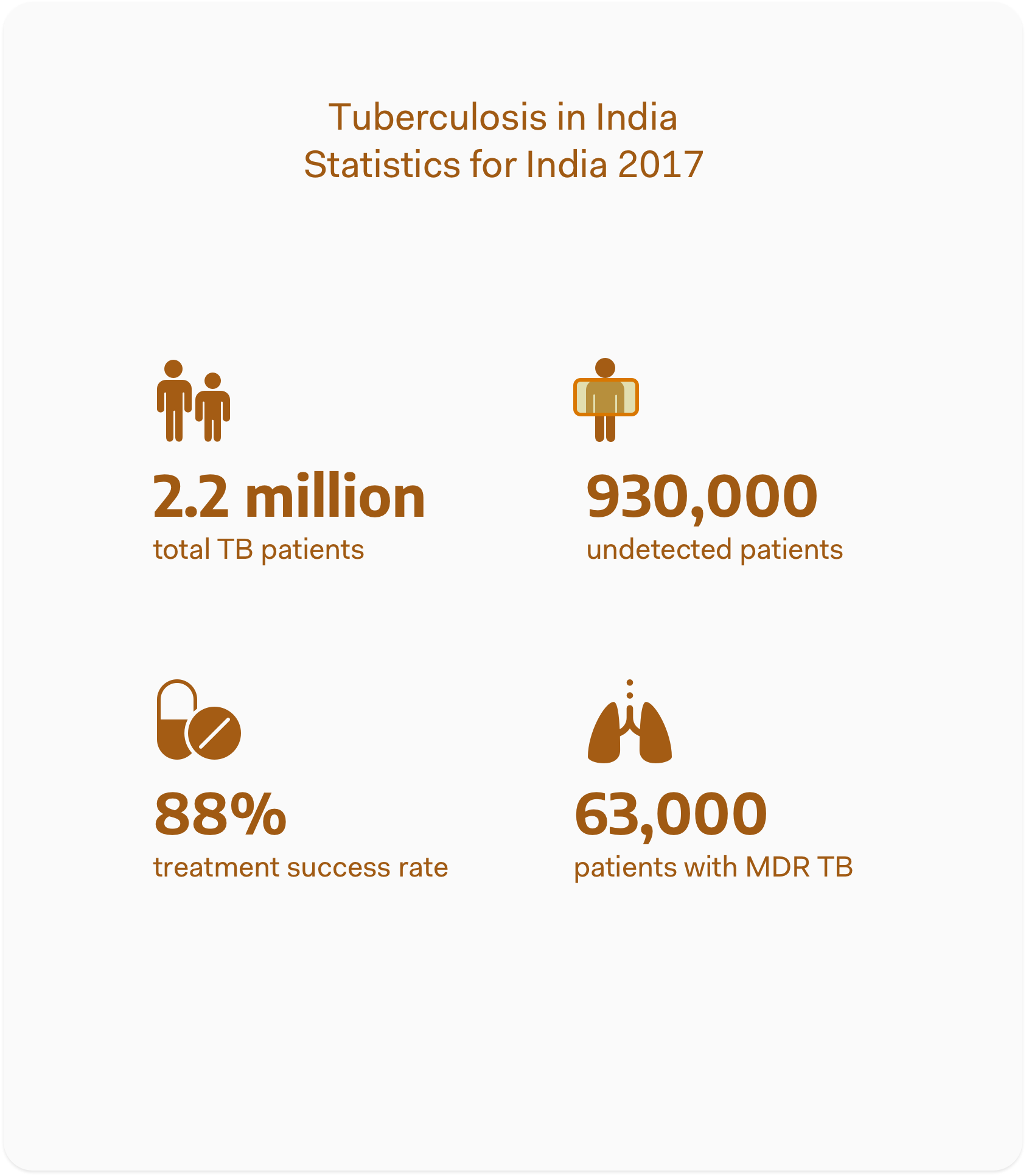
Case for India
Relevant Solutions
India accounts for a quarter of the TB patients worldwide. India also has the highest number of Multidrug-resistant TB patients in the world. India however is also in the forefront of addressing the TB menace. India has taken concerted steps to eradicate TB by the year 2025.